TRADEMARK (TM)
A word, device, number, symbol, distinctive shape, color, or any combination of these used to identify goods or services and distinguish them from similar goods or services.

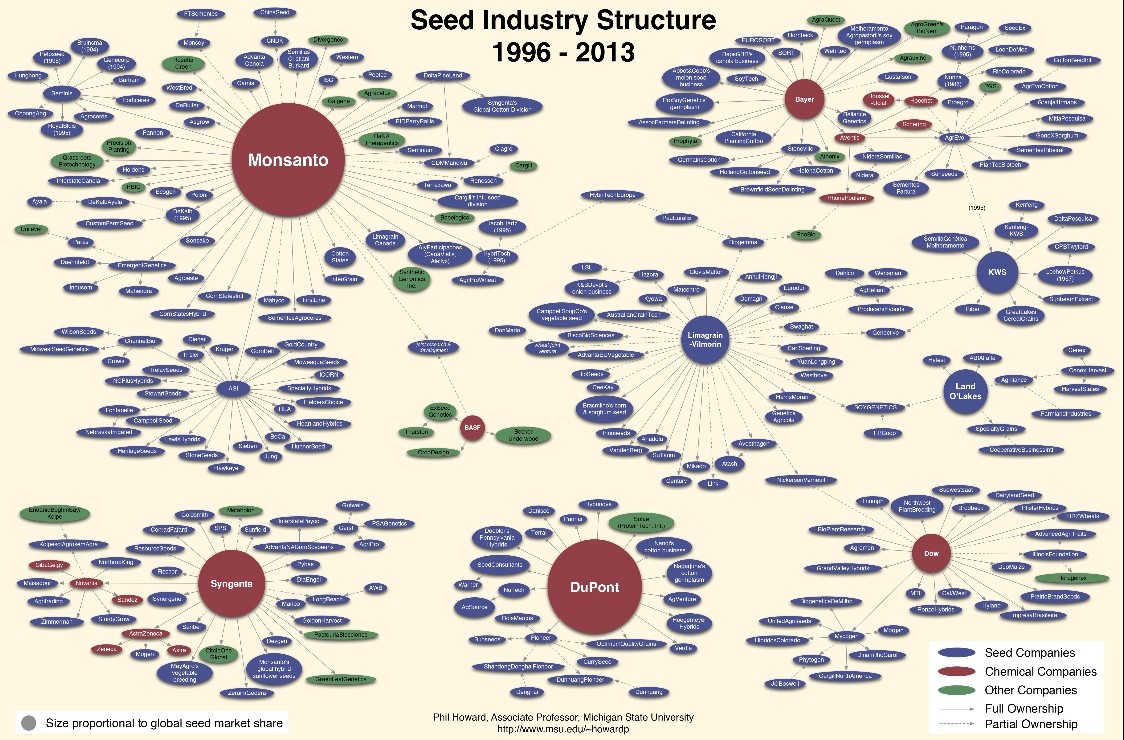
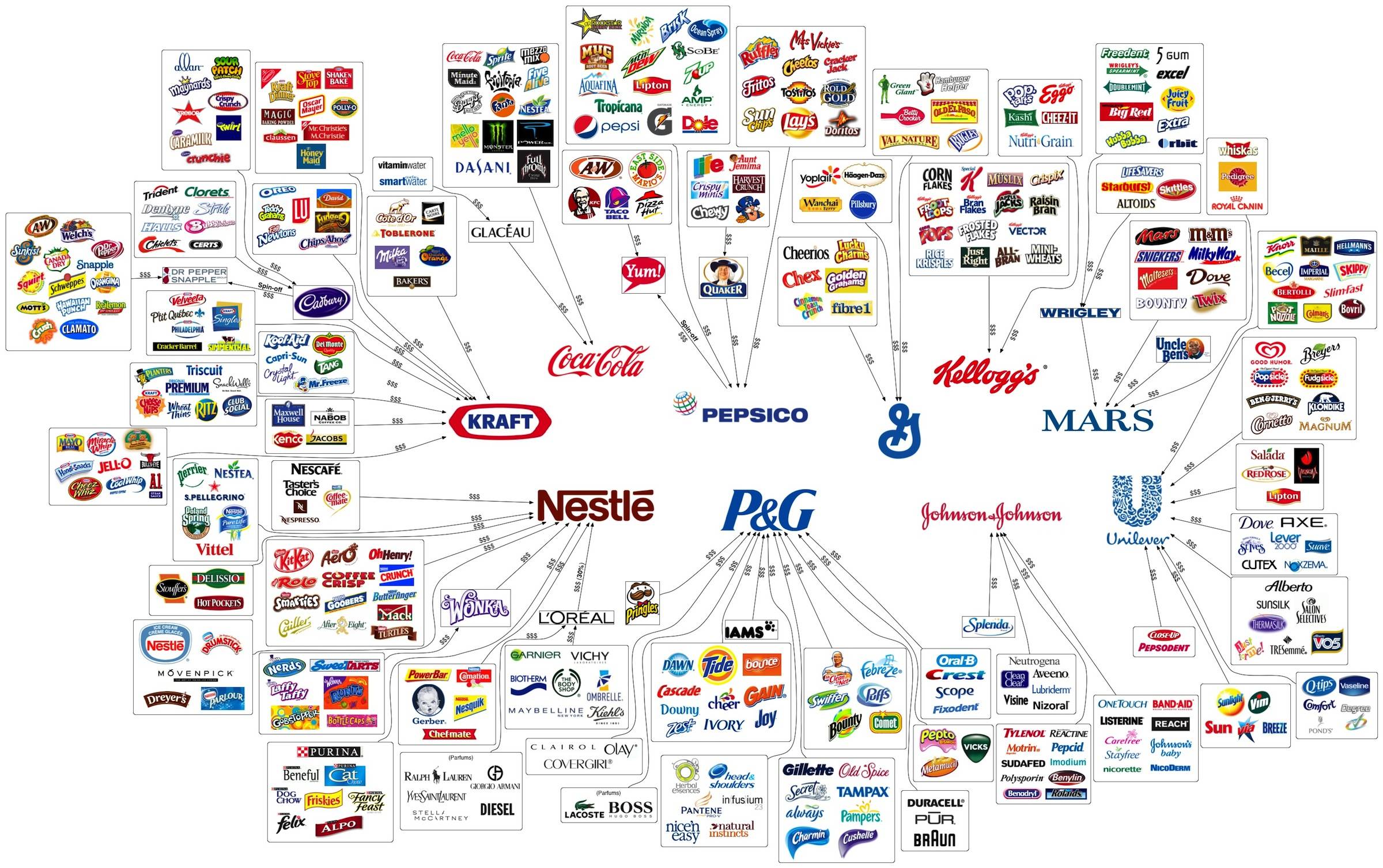
- Granted to reduce confusion in the marketplace by preventing the unlicensed use of the registered mark, or one of a similar nature, on goods which are the same or similar to those for which the mark is registered.
- Trademarks developed from the common law action of passing off, which was an action to prevent the unfair competitive practice of filching another’s commercial reputation.
- PRODUCT DIFFERENTIATION...
- 'Shorthand’ upon which consumers can rely in making rational product selections.
- PVP certified variety names (7 USC §2422) may be given trademark protection.
- In many countries, exclusive rights in a trademark are acquired from the moment of first use. However, registration of the mark invariably confers stronger rights than mere user rights.
- Unlike other forms of IP protection, a trademark can generally be kept alive forever, provided its use is safeguarded and renewal fees are paid. Trademark law, unlike patent and copyright, confers a perpetual right. A federal trademark registration has an initial term of 10 years, with available 10-year renewal terms.
‘Service marks’ (SM) use similar devices to identify and distinguish the services of one entity from those of others. In contrast, ‘trade names’ identify the entity itself rather than the goods or services it provides.


- Finally, ‘trade dress’ signifies a product’s shape, colour, packaging and overall appearance, which may serve as a designator of the origin or manufacturer of a product.